Causes of Arthropathy
Regeneration of hyaline cartilage requires collagen, which is produced in the body with the participation of the liver. This organ is not only involved in the synthesis of collagen, which is essential for joints, but is also responsible for body heat levels. From a medical point of view, the cause of all cold illnesses, including joint disease, is a decrease in heat levels in the body. This may occur especially due to insufficient liver function.
- overweight,
- unhealthy diet
- Heavy physical labor, strenuous exercise,
- Trauma, multiple microtrauma,
- exposed to cold
- age-related body changes (dehydration),
- Congenital anomalies (dysplasia, connective tissue weakness, etc. ).
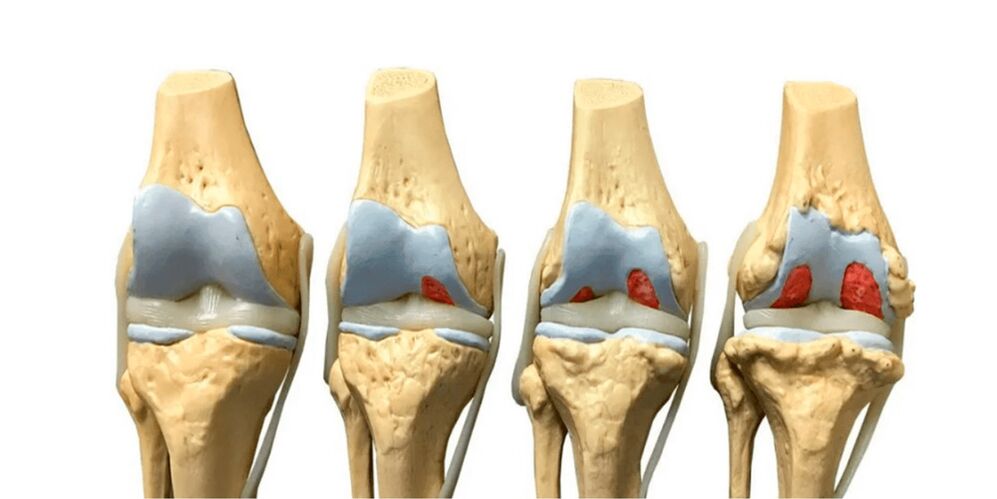
Classification
Symptoms of Arthropathy
diagnosis
At the first visit, the doctor usually asks the patient not only about the symptoms of arthrosis, but also about the nature of the patient's nutrition and lifestyle, since in Eastern medicine the human body is considered a single system. There are inherent connections in this unified system. For example, the condition of joints is closely dependent on metabolism, immunity, hormonal systems and fluid movement, body mass index. Modern medicine classifies joint diseases as cold diseases, which occur due to the body's energy depletion, decreased heat, and accumulation of cold air. The key factors causing this are poor eating habits, sedentary lifestyle, exposure to cold and dampness, etc.
Treatment of Arthropathy
- drug.Medications are used to relieve symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. In the presence of an inflammatory process, hormonal (glucocorticoids) or nonsteroidal drugs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs based on ibuprofen, diclofenac, etc. ) are prescribed. Typically, these drugs are given by injection into a joint or into a muscle. To slow down the process of joint cartilage destruction, chondroprotectants are used.
- Injected into the joint.To reduce friction and improve sliding, hyaluronic acid is injected into the joint space, and its molecules have the ability to retain moisture. Injections of hyaluronic acid protect the cartilage surface from drying out and slow its destruction.
In cases where severe inflammation and swelling are present, hormonal medications may be injected into the joint space. - Operation.Surgical treatment of arthrosis involves replacement of the joint with an endoprosthesis. Such interventions are indicated in the fourth stage of the cataleptic (total immobility) disease.
- physiotherapy.To relieve inflammation, physical treatments such as laser therapy, magnet therapy, and medications using electrical current (electrophoresis) or ultrasound (phonotherapy) can be used.
Mud application, compression, and heat improve local blood circulation, promote healing and recovery of cartilage tissue, and relieve pain. - Other treatments.For the prevention of joint diseases, as well as as an adjunct to therapeutic methods, exercise therapy (physiotherapy) is prescribed. Performing simple exercises regularly can improve blood supply to your joints, increasing their flexibility and range of motion.
A hot bath can be used to warm painful joints and relieve symptoms. Balneotherapy treatments for arthritis include treatments such as mud baths or radon baths.
This is important! Chondroprotectants do not affect the cause of arthropathy. In essence, these are not therapeutic agents, but preventive agents. They contain chondroitin and glucosamine, which increase the amount of lubrication (synovial fluid) and promote gliding. Reducing friction can slow the destruction of cartilage, but it cannot restore it. In order not only to slow down the progression of the disease, but also to reverse it, it is necessary to improve the blood supply, activate metabolism and tissue regeneration processes. Chondroprotectants don't do that. Therefore, they can be used as adjunctive treatments but are not a substitute for comprehensive treatment.
Treatment of joint diseases in specialized clinics
Joint disease refers to the imbalance of Bad Kan, one of the three major control systems of the body. The balance of Bad Kan means health, and the imbalance means disease. In addition to joints, this foundation is responsible for the lymphatic system, fluids, immunity, hormones, and metabolism. Bad Kan imbalances often lead not to one disease but to several diseases at once. Therefore, arthropathy is almost always accompanied by concomitant conditions, diseases, such as overweight (obesity), chronic respiratory diseases, allergic and/or immunodeficiency conditions, endocrine disorders, hormone-dependent gynecological diseases (in women), etc. Modern treatments can restore the balance of the entire Bad Kan base, thus eliminating the common cause of all these diseases. Therefore, in addition to arthropathy, other concomitant diseases may occur. When treating arthropathy, doctors treat not only the affected joint area, but also the entire body to restore the balance of the Badeck base. This is the secret to the effectiveness of joint treatment in our clinic.