- Stage I - There is a "crack" in the annulus fibrosus and the nucleus pulposus moves within the intervertebral disc, but there are no radiological signs yet;
- Stage 2 - The nucleus pulposus continues to deteriorate, the intervertebral disc height decreases, the annulus fibrosus "dries out", and the affected intervertebral joints become unstable. To compensate for this, the back muscles continue to tense, leading to pain and "overexertion", Signs of osteochondrosis may be seen on radiographs;
- Stage III - Disc rupture and herniation of the prolapsed nucleus pulposus, this stage is characterized by extensive neurological symptoms, inflammation and edema;
- Stage 4 - Lesions involve adjacent elements of the joint.
- Cervical Vertebrae - most commonly located between the fifth and seventh cervical vertebrae (the most mobile joint);
- Chest - a variant manifested by pain, which may be confused with diseases of other organs of the chest;
- Lumbar spine - the most common type, due to the greatest mobility of this part and the loads placed on it;
- Common - multiple segments involved (e. g. cervicothoracic segment).
Causes of osteochondrosis
- Excessive stress, physical labor, and occupational hazards (carrying heavy objects) are common causes of osteochondrosis in men;
- spinal injuries;
- Violent and uneven jerking, bending, and turning of the body;
- Sedentary work and lack of physical activity;
- Repeated movements (carrying a bag on the same shoulder, tilting head to ear while talking on the phone);
- climate conditions.
- Men (osteochondrosis occurs less frequently in women);
- Being overweight and tall;
- Abnormal development of the musculoskeletal system and weakness of the back muscles;
- bad posture;
- Leg disorders (arthritis, flat feet);
- Violates the nutritional function of intervertebral joints;
- Pathology of internal organs.
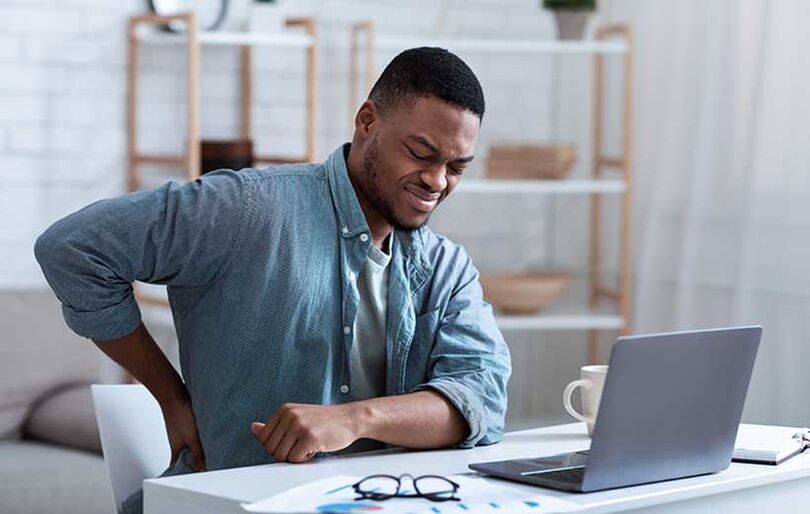
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
- Neuro-orthopedics, which evaluates the static and dynamic functions of the spine (posture, presence of scoliosis, muscle tone, and range of motion of intervertebral joints and limbs);
- Neurology – Reflexes and compressed vertebral syndromes, motor and sensory functions, determination of tissue nutritional quality.